The integration of digital technologies into manufacturing processes led to the creation of smart factories that are more efficient, productive, and cost-effective, giving rise to what is commonly known as Industry 4.0 or the Fourth Industrial Revolution. Technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, big data analytics, and the Internet of Things (IoT) are also paving the way for new business models and revenue streams through greater automation, flexibility, and customization. In this article, we will focus on the role of IoT in transforming the manufacturing industry.
IoT refers to the network of physical devices, appliances, vehicles, buildings, and other objects that are embedded with sensors, software, and connectivity, enabling them to exchange data and communicate with each other. According to a recent report by McKinsey, the global IoT market for manufacturing is expected to grow to $438 billion by 2025, up from $183 billion in 2019.
IoT or IIoT?
IoT is a broad term that covers a wide range of applications but is commonly associated with consumer use and typically used for applications such as home automation, wearables, and smart appliances. Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) refers to the use of IoT technologies in industrial settings such as manufacturing plants, oil rigs, and transportation systems. IIoT devices are often designed to withstand harsh environments and used for applications such as equipment monitoring, predictive maintenance, and supply chain management. They are typically more complex and specialized than consumer oriented IoT devices, and they often require integration with existing industrial control systems. The data collected from IIoT can be used to improve efficiency, productivity, quality, and safety.
How does IIoT help with digital transformation of manufacturing industry?
Data-driven decision-making is crucial for the success of digital transformation. The IIoT stands out in its ability to gather data through sensors and telematic devices, allowing organizations to examine the information derived from their industrial operations and resources. By harnessing the capabilities of analytics driven by AI and machine learning, manufacturers can automatically identify irregularities, enhance process efficiency, and elevate the overall quality of their output.
A study by MCKinsey (The age of analytics: Competing in a data-driven world) highlights that manufacturers can reduce operating costs by up to 25%, reduce development costs by up to 50%, and increase gross margins by up to 30% by capturing the value of data and analytics. Here are some ways IIoT can help with digital transformation.
- Data collection and analysis: Data collected by IIoT devices on industrial processes, equipment performance, and environmental conditions enable organizations to identify patterns, trends, and anomalies. These insights can be used to reduce downtime and improve efficiency.
- Predictive maintenance: By monitoring equipment performance in real time and predicting maintenance requirements, manufacturers can reduce downtime and improve asset utilization.
- Quality control: Various sensors help monitor several variables that measure product quality in real-time. Manufacturers can use this data to detect defects and take corrective actions immediately, improving product quality and customer satisfaction.
- Supply chain optimization: IIoT devices can track inventory levels, monitor shipping and receiving, and optimize logistics to improve supply chain visibility, reduce waste, and enhance customer satisfaction.
- Asset tracking: IIoT devices can monitor the location of assets such as tools and equipment, throughout the manufacturing process, providing valuable insights into their location, usage, and performance.
How is data collected with IIoT devices stored and analyzed?
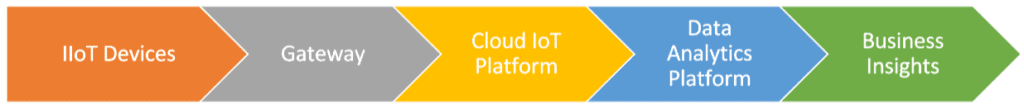
IIoT data is collected and stored through a combination of sensors, gateways, and cloud-based platforms. The process of collecting data begins with the installation of sensors on machines, equipment, and other assets. These sensors are designed to gather data on various aspects of the manufacturing processes such as temperature, pressure, vibration, and energy consumption, which is transmitted to a gateway device. The gateway device consolidates the data from multiple devices into a single data stream and transmits it to cloud-based platforms such as Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure, where it is stored and processed.
By leveraging techniques such as machine learning and statistical modeling, the analytics platform uncovers patterns, trends, anomalies, and correlations within the data. With real-time and historical analytics, businesses can gain a comprehensive understanding of their operations.
The data analytics platform supports integration with other business systems and tools, facilitating seamless data flow across the organization. It enables stakeholders from various departments to access and utilize the actionable insights derived from IoT data driving business growth and competitiveness.

What are the challenges to implementing IIoT in manufacturing?
Although IIoT is transforming the way factories operate, implementing IIoT in manufacturing comes with its fair share of hurdles. Here are some challenges that the manufacturers face with extracting value from IIoT in their operations:
- Capital Intensity: The implementation of IIoT in manufacturing may require significant capital investment, as it entails expenses for devices, infrastructure, and training needed to effectively operate and maintain the system. Upgrading legacy systems that are incompatible with IoT technology may necessitate substantial financial commitments by companies.
- Integration: One of the biggest challenges is integrating IoT technology into existing manufacturing systems that may not have been designed with IoT in mind. Ensuring seamless data exchange and communication between disparate systems can be a complex task, requiring careful planning, expertise, and collaboration among various stakeholders.
- Data Security: As IIoT devices are connected to the internet, they are susceptible to cyber-attacks, which can be a significant concern for manufacturing companies that handle sensitive information. Strong device authentication, encryption, access controls, and regular security audits need to be implemented to ensure data privacy and system integrity.
- Data Management and Analytics: IoT devices generate a vast amount of data. Strong expertise is needed to manage this data and establish advanced analytics capabilities to extract insights that can drive decision-making.
Beginning the IIoT journey: Key considerations and first steps
Initiating IIoT implementation in manufacturing can be as straightforward as deploying a handful of sensors to gather data on a particular process or equipment. Nonetheless, enterprises must have a clear understanding of their objectives and how IIoT can aid in their attainment. Moreover, it is highly advisable to collaborate with reliable partners who can assist in navigating the intricacies associated with the adoption of novel technologies.
- Define Objectives and Use Cases: Begin by identifying the specific objectives and use cases for IIoT. Determine the areas where IIoT can bring value and define goals such as improving operational efficiency, reducing costs, increasing product quality, or enhancing customer experience.
- Conduct a Feasibility Study: Assess the technical and financial feasibility of implementing IIoT, considering factors such as current and new infrastructure, connectivity, security, data management, and cost. It is also important to evaluate the integration capabilities of new infrastructure with existing systems.
- Choose IoT Platform: Identify a platform that aligns with their business objectives and requirements and provides the necessary tools to collect, store, manage, and analyze data from IoT devices. Some leading IoT platforms are Microsoft Azure IoT, AWS IoT Core, and PTC ThingWorx.
- Create a Data Analytics Framework for Insights: Develop a data analytics platform to gain insights from the collected data. This includes using machine learning algorithms, statistical analysis, and visualization techniques to extract meaningful information, identify patterns, and derive actionable insights.
- Integrate with Existing Systems: Integrate IIoT data and insights with existing manufacturing systems such as enterprise resource planning (ERP), manufacturing execution systems (MES), or maintenance management systems. This enables seamless information exchange and decision-making across different organizational functions.
- Conduct a Pilot Test and Scale up: Test the feasibility of the IIoT solution by deploying a small-scale system to validate its functionality and demonstrate its value. Refine the implementation approach as needed and gradually scale up the deployment across different areas or facilities.
- Monitor and Optimize: Continuously monitor the IIoT infrastructure, data quality, and performance. Identify opportunities for improvement by analyzing data generated by IIoT devices, identifying patterns and insights, and using this information to optimize operations and improve business outcomes.
Summary
Integration of IoT technologies into manufacturing processes has revolutionized the industry, leading to the creation of smart factories and the rise of the Fourth Industrial Revolution. IIoT has enabled manufacturers to collect and analyze data on industrial processes and assets, automating anomaly detection, optimizing processes, and improving quality resulting in lower operating costs, increased gross margins, and enhanced customer satisfaction.
However, implementing IIoT in manufacturing is not without its challenges. Capital investments, integration complexities, data security concerns, and data management challenges pose significant hurdles. By starting with smaller-scale deployments and collaborating with trusted partners, management can ensure successful implementation of IIoT within their organization. This measured approach allows for controlled, gradual rollout and provides valuable expertise to navigate the intricacies associated with IIoT integration, ensuring long-term success and maximum benefits.
Backed by its industry expertise in delivering business impact, QX Impact assists with digital transformation of small and mid-size manufacturers.


